Diabetes mellitus
More commonly referred to as "diabetes" -- a chronic disease associated with abnormally high levels of the sugar glucose in the blood.
When you eat food that contains carbohydrates it's broken down in the stomach and digestive system into glucose, which is a type of sugar. We need glucose from food because that's what gives us energy. Carbohydrate containing foods are things like starchy foods, sugary foods, milk, and some dairy products and fruit.

This glucose then moves into the bloodstream and the body detects that the blood glucose level is rising. In response to that the pancreas, which is a little gland that sits just underneath the stomach, starts to release a hormone called insulin and it's insulin that helps our body get the energy from the food we eat. The bloodstream then takes the glucose and the insulin to every cell in our body that needs it.
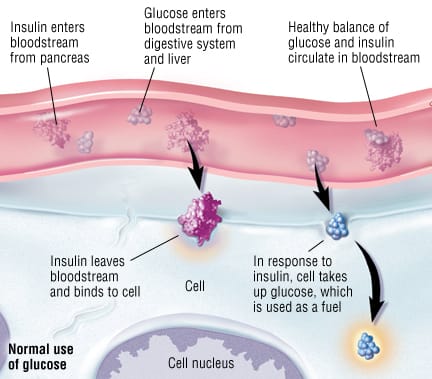
To make this easier to understand let's see at muscle cells. At the muscle cells, it's insulin that allows the glucose to get into the cells where it can be used for energy. It's a bit like insulin is a key unlocking the door to the cells so the glucose can get in. That way, the blood glucose levels start to drop but the blood glucose level can be topped up at any point by the liver releasing extra glucose that it has stored.
The blood glucose rises again, and again, the pancreas produces more insulin to move with that glucose through the bloodstream to the muscle cells, open the doors and let the glucose in. The body functions best with blood glucose at an optimum level. It doesn't like it if the blood glucose rises too high. Normally there's a cycle within the body that balances out the glucose and the insulin level and this is achieved the food you eat, the pancreas, and the liver. However, in some people, the system doesn't work properly and they develop diabetes.
There are two main types of diabetes -
Type-1 diabetes(juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes)
Type 1 diabetes accounts for about 10 percent of all cases. It's most often found in the under the 40s and it's by far the most common type of diabetes found in childhood.
Causes of type-1 diabetes
In Type 1 diabetes the body isn't making any insulin at all. This is because of an autoimmune response whereby the body has destroyed the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. We don't entirely know why that happens in some people and not in others.

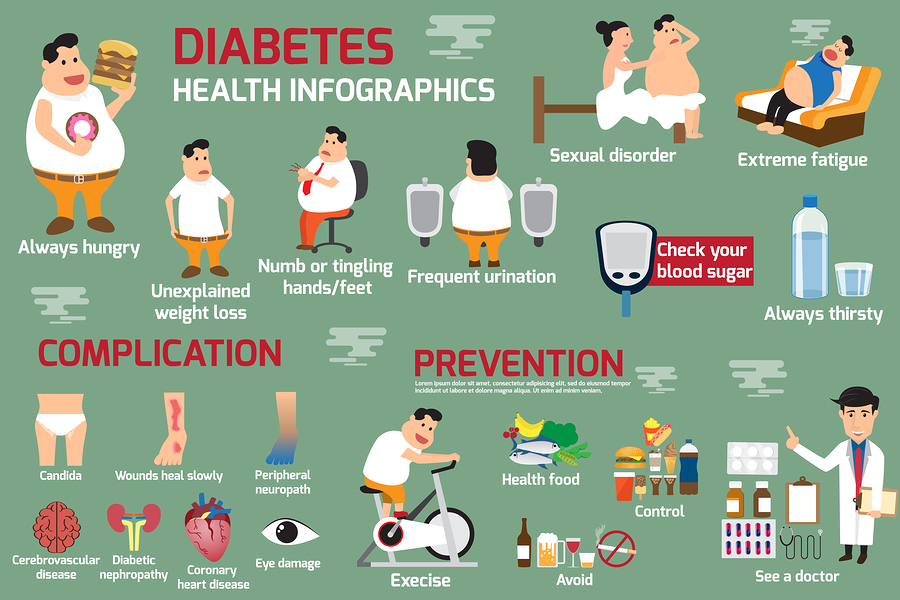
In Type 1 diabetes the carbohydrate-containing food is turned into glucose as normal. That glucose then moves into the bloodstream. Normally the body would produce insulin to let that glucose into the cells but because into the cells but in Type 1 diabetes there is no insulin being produced so the glucose can't get into the body cells at all, so the level of glucose in the blood rises and rises. The body tries to lower the level of glucose, it tries to get rid of the glucose through the kidneys. That's why people who have undiagnosed type 1 diabetes tend to go to the toilet a lot to pass urine. As the kidneys filter the glucose out of the blood, they also take a lot of water with it so the person with diabetes will get very thirsty. The urine contains a lot of glucose and that creates an environment where it's quite easy for bacteria to thrive so it's also quite common to get thrush or genital itching. In the same way, the blood contains a high level of glucose as well so more bacteria than usual will tend to breed in flesh wounds and they might be slow to heal. Glucose can also build up in the lens at the front of the eye causing the liquid in the lens to become cloudy. That can mean that some people with undiagnosed Type 1 diabetes can have blurred vision. Because the glucose can't get into the cells to be used for energy, somebody who's got undiagnosed Type 1 diabetes is going to start feeling very tired, lethargic, and unable to go about their normal daily routine. But the body still needs an energy source in order to work properly so what it does is it starts to break down its fats tools and that can lead to weight loss.
The main symptoms of Type-1 diabetes are-
- going to the toilet a lot,
- thirst,
- thrush or genital itching,
- slow healing of wounds,
- blurred vision tiredness
- weight loss.
These symptoms generally happen quite quickly often over a few weeks and come be reversed once the diabetes is treated with insulin.
Type 2 diabetes(adult-onset diabetes)
Type 2 diabetes accounts for about90 percent of all cases in the population. It's most common in the over 40 age group in the white population and in the over 25 age group in theSouth Asian population.
Causes of type-2 diabetes-
Type 2 diabetes is a little more complex because there are slightly more processes at work. Either the body isn't producing quite enough insulin or the insulin it is producing networking properly.
That can be due to being overweight because a build-up of fat can stop insulin doing its job properly but it can also happen in people of a healthy weight. So in Type 2 diabetes, the carbohydrate-containing food is broken down into glucose in the stomach and digestive system as normal. That glucose then moves into the bloodstream. The pancreas starts to produce insulin which moves with the glucose through the bloodstream to all the body cells which need glucose for energy. However, the glucose can't always get into the cells because the locks to the cell doors have become furred up with fat deposits.
That means that the insulin can't open the cell doors properly. So the level of glucose in the blood continues to rise. In response to this, the pancreas produces even more insulin so the blood glucose levels continue to rise and the insulin levels continue to rise. This situation is further complicated by the cells which are desperate for energy - sending out emergency signals to the liver to release stored glucose. The blood glucose level up and up and the pancreas produces more and more insulin until it can't cope anymore and eventually it can wear out.
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes are-
- going to the toilet a lot
- thirst,
- thrush or genital itching,
- slow healing of wounds,
- blurred vision,
- tiredness,
- weight loss in some people.
The symptoms for Type 2 diabetes come along very slowly and some people don thave any symptoms at all. So for that reason, people can live withType 2 diabetes for up to 10 years before they realize that they have it.
Treatments of type-2 diabetes
Type2 diabetes can be treated in a number of different ways. Initially, it may be sufficient to make changes to the food you're eating and to take extra physical activity or lose any weight that may be appropriate. But Type 2diabetes is a progressive condition and most people will need some form of medication to treat.
Preventive measures-
- Check your risk of diabetes. Take a life risk assessment test and learn more about your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Manage your weight. Excess body fat, particularly if stored around the abdomen, can increase the body’s resistance to the hormone insulin. This can lead to type 2 diabetes.
- Exercise regularly. Moderate physical activity on most days of the week helps manage weight, reduce blood glucose levels, and may also improve blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Eat a balanced, healthy diet. Reduce the amount of fat in your diet, especially saturated and trans fats. Eat more fruit, vegetables, and high-fiber foods. Cut back on salt.
- Limit takeaway and processed foods. ‘Convenience meals’ are usually high in salt, fat, and kilojoules. It’s best to cook for yourself using fresh ingredients whenever possible.
- Limit your alcohol intake. Too much alcohol can lead to weight gain and may increase your blood pressure and triglyceride levels. Men should have no more than two standard drinks a day and women should have no more than one.
- Quit smoking. Smokers are twice as likely to develop diabetes as non-smokers.
- Control your blood pressure. Most people can do this with regular exercise, a balanced diet, and keeping a healthy weight. In some cases, you might need medication prescribed by your doctor.
- Reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease have many risk factors in common, including obesity and physical inactivity.
- See your doctor for regular check-ups. As you get older, it’s a good idea to regularly check your blood glucose, blood pressure, and blood cholesterol levels.







Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any doubt, feel free to comment.